Ingredients Penetration Enhancer Systems -
Liposome Delivery System
Liposomes are small, spherical vesicles which consist of amphiphilic (both water and fat soluble, as opposed to hydrophobic and hydrophillic) lipids, enclosing an aqueous core. The lipids are predominantly phospholipids (e.g. lecithin) which form bilayers similar to those found in biomembranes. In most cases the major component is phosphatidyl choline (lecithin). Depending on the processing conditions and the chemical composition, liposomes are formed with one or several concentric bilayers.
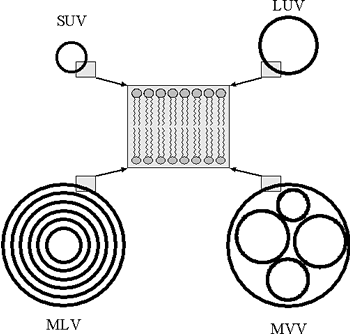
Liposomes are often distinguished according to their number of lamellae and size. Small unilamellar vesicles (SUV), large unilamellar vesicles (LUV) and large multilamellar vesicles (MLV) or multivesicular vesicles (MVV) are differentiated (see figure). SUVs show a diameter of 20 to approximately 100 nm. LUVs, MLVs, and MVVs range in size from a few hundred nanometers to several microns. The thickness of the membrane (phospholipid bilayer) measures approximately 5 to 6 nm.
Large liposomes form spontaneously when phospholipids are dispersed in water above their phase transition temperature. The preparation of SUVs starts usually with MLVs, which then are transformed into small vesicles using an appropriate manufacturing technique, e.g. high-pressure homogenization.
Nonphospholipid liposomes include Niosomes and sphingosomes which are vesicles with a similar structure. In contrast to lecithin (phospholipids) based liposomes, nonionic surfactants, e.g. polyglyceryl alkyl ethers, or sphingolipids make up the bilayer of niosomes and sphingosomes, respectively.
Liposomes which are used as delivery systems, may encapsulate hydrophilic (water soluble) substances in their aqueous core. Amphiphilic (both water and fat soluble) and lipophilic (hydrophobic. i.e. fat soluble) substances, e.g. oil soluble UV filters, can be incorporated into the lipid bilayer. Loaded liposomes as well as non-loaded, empty liposomes, are used in cosmetics. The major effect of empty liposomes is an increase in skin humidity.
Liposomes are an important component of many skin rejuvenation treatments because of the ability of liposomes to encapsulate active anti-aging ingredients and deliver them through the layers of skin right down to the cellular level where they can do the most good. They can easily penetrate through the layer of the skin. Based on this feature, active ingredients can be incorporated into liposomes to enhance their absorption by the skin and thus their efficacy. In fact, liposome-encapsulation largely reduces the amount of the active ingredient required for effectivness as compared to non- encapsulated, pure active ingredients. This special delivery system serves to provide cells with critical nutrients and the nourishment necessary to promote collagen production.
The skin compatibility of topically applied phospholipids is very high. There are no restrictions concerning their use in foodstuff and cosmetics, neither in the EU nor for regulations of the US Food and Drug Administration; lecithins are generally accepted as safe (GRAS status – Generally Recognized As Safe). However, it is known that high doses of phospholipids which are applied topically over a longer period may lead to irritations on dry and normal skin.